Neighbouring Countries









Neighbouring Countries
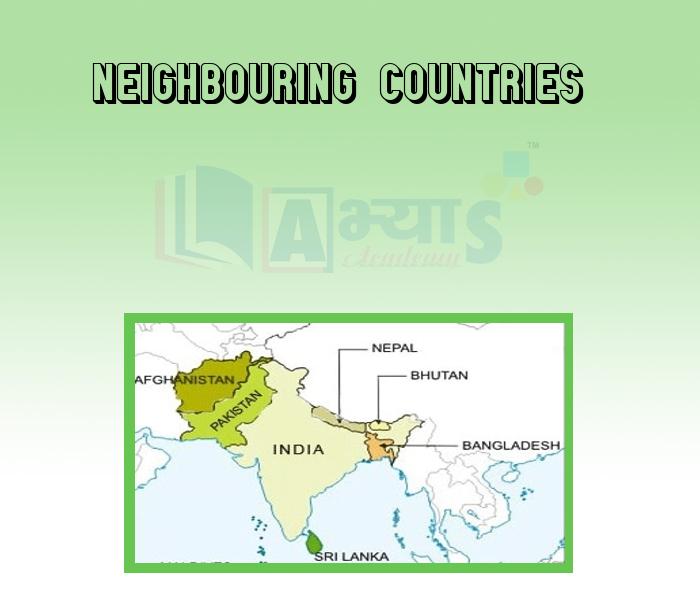
India is bounded by the Muztagh Ata, Aghil and Kurlun mountains to the north of Kashmir. She has Zaskar Mountains on the east side of Himachal Pradesh/and northern side of Uttar Pradesh. For the rest, Himalayas form her boundary in the Nepal region. In the north, India is adjoined by China, Nepal and Bhutan. In the east lie Bangladesh and Myanmar (Burma). Afghanistan and Pakistan border on the north-west. The Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait separate India from Sri Lanka in the south. The Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal and Lakshadweep in the Arabian Sea also constitute parts of the territory of India.
Pakistan, Afghanistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar and Bangladesh are seven neighboring counties located in the India's terrestrial border, with the length of India's border being respectively 3,310 km, 106 km, 3,917 km, 1,752 km, 587 km, 1,458 km and 4,096 km respectively.
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
It was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.
